Creating and editing a form
1. General
The number of forms a user can create is not usually restricted. When designing a new form or wishing to see the functions of E-lomake, you can always create a new form or use a form you have created for practicing purposes.
2. Creating a new form
You can create a new form by clicking the New form tab. All the forms you have created or have the right to use are under the Forms tab.
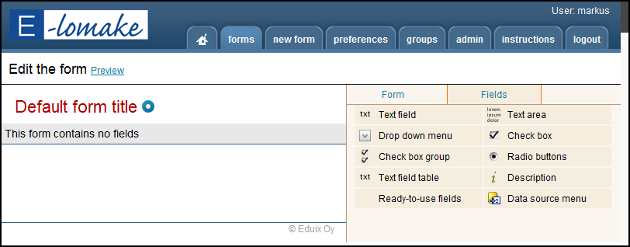
After you have clicked the New form tab, you can immediately begin editing the form. You do not have to save the form separately; all changes are saved as you work on the form.
At first, the field only shows the default form title. You can start by clicking the blue dot next to the title and giving the form a title, such as Enrolment for staff training 1.1.2011.
You can also give the form a name which is only visible for the administrators, such as Customer form H001. The name and title allow you to identify the form from the list of forms on the Forms tab.
Use the tabs on the right side of the screen to edit the form: Form and Fields. The link Preview allows you to see what your form will look like.
You can create a form in any order you wish to. The form creation is divided into three steps:
1. Creating the structure of the form
2. Editing the settings of the form
3. Publishing the form
2.1 Creating the structure of the form
When planning the fields needed in the form, you should begin by thinking how the data will be used:
1. What information do you need
2. What information is mandatory
3. Which pieces of data needs restrictions (e.g. length, only numbers)
Adding a new field is done by clicking the name of the desired field time on the Fields tab. The settings differ from one field type to another, and you can get more detailed instructions by clicking on the question mark (?) next to the setting.
![]() You can easily copy the fields and field groups you have made (
You can easily copy the fields and field groups you have made ( ![]() ) as well as to change their order by dragging with the mouse (
) as well as to change their order by dragging with the mouse ( ![]() )
)
The most common settings (only header and field group are mandatory):
Header
The title shown on the field (for example: Address)
Name
The name of the field is used in the database views
Location
Is the header shown next to the field or above it
Description
Only visible to the administrators of the form. You can use this for notes or for explaining the field to the other administrators.
Help desk
The instructions shown to the recipients when they click the question mark symbol.
Default/Length/Width
The size of the field on-screen (don’t change the value, if the field doesn’t seem too small. Different browsers may display fields in different ways.)
Max
How many characters can the respondent enter into the field (please note that names and especially e-mail addresses can be surprisingly long.)
Verification
The respondent can only fill in certain values into the field (e.g. numbers, Finnish personal identification number or a zip code). If you select Date verification, the published form shows a link to select the date from a calendar view.
Field is required
The respondent must fill in a value/select from the options. Different field types also allow you to set limits to the selection (the minimum and maximum number of selections).
Password field
The text entered into the field is hidden from the respondent, meaning that when it is entered, only asterisks (******) or bullets are shown.
Functions
Recipient – after the reply, an e-mail is sent to the e-mail address entered into this field. The content of the message is defined in the form settings under Feedback – Email message to the respondent.
The field is typically used, when the respondents need to get the information they have entered into their own e-mail as well. The same message can also contain information on what steps will be taken next. (For example: Thank you for your feedback! We will get in touch with you soon. The information you gave:…)
Field group
Place the fields belonging under the same topic into the same field group (e.g. contact information). You can share field groups or use fields created by others – field groups are also essential when creating dependencies or processing phases.
![]() Example: you wish to add the fields name, e-mail address and message onto your form.
Example: you wish to add the fields name, e-mail address and message onto your form.
1. Click the tab Fields on the right side of the window.
2. Select text field, define the header as Name, mark the field required, group: contact information - > Save
3. Select text field again, header E-Mail, verification: Email address and Function Recipient, group: contact information -> Save
4. Select text field, header Message, mark the field required, group: contact information -> Save
5. Add descriptions, if you wish to add information between the fields in the form -> save and drag to the correct place with the mouse.
In the editing state of the field group (edit button on the header row of the field group) you can define the visibility of the field group:
Displayed normally – the field group is visible both to the respondents and the administrators
Header not displayed – the field group is displayed but its header is hidden.
Hide from the respondent – the respondents don’t see the field group at all.
A hidden field group can be used to help with handling the inputted data (for example: making a note who got in contact with the recipient, and what was agreed: hidden field group Actions and fields Handler and Agreed).
2.2 Editing the form settings
The form settings can be found under the Form tab on the right side of the screen.
• Form text
- Form name – only displayed to the administrators of the form
- Form header – displayed to the recipients as the title of the form
- Description – text displayed after the header
- Preface – text displayed above the header
- Epilogue – text displayed below the form
• Parallel forms
- With parallel forms, you can e.g. create the same form in different languages or give different instructions to different recipient groups.
- See instructions: parallel forms
• Feedback
- Define the web-page and text which are displayed to the recipient after they have replied. You can also define an e-mail message to the respondent.
- The sender of the e-mail is, by default, the e-mail address of the form’s creator.
• Submission processing
- Create a workflow for the form. The form is submitted from one handler to another.
- See instructions: Processing phases
• Registry description
- Create a registry description for the form.
• Appearance
- Select how the form is displayed: all in one page or paging by field groups.
- Select the style you wish to use.
- Define the measurements for the form and fields.
• Permissions
- Select the users who get an e-mail when the form is saved.
- Select the users who have the right to maintain the form
- Select the users who have the right to read the reports of the form.
- See instructions: User settings and usage right levels
• Removing submissions
- The respondent may remove the submission they have made if this function is used
- The form must contain a field for an e-mail address. This field must be defined as required, verified (e-mail address) and needs the function Recipient.
- Select also one or more fields which the respondent has to re-fill in to ensure the removal.
• Dependencies
- By using dependencies, you can create a form where certain field groups are only shown to certain respondents.
- Example: if the respondent has filled in their age as less than 18, the field group Parent’s contact information is shown.
• Saving and files
- May the respondent add attachments
- Can the respondent continue the form submission later
- The printing format (RTF file base)
- Additional information to be saved (e.g. respondent’s IP address)
- Can the report be used in other applications
2.3 Publishing the form
In the tab Forms you can see all the forms you have created as well as the forms you can maintain. The contents of the form listing:
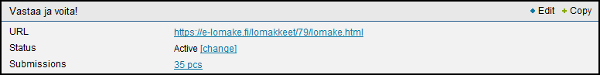
• Header of the form
• The web address, where the form will be once it has been published
• Editing, copying and removing the form
• Status of the form– select change when you want to publish the form or remove it from publicity
See publishing instructions: Publishing and timing forms
3. Reusing field groups
Reusing the field groups aims to make the work of form creators easier as well as to ensure the usability of the data being collected. Your organization may, for example, want to get specific contact information from all clients. The form and necessity of the data has been carefully thought out so that transferring the data into another system will be easy.
A lot of the data being collected is such that you know many other form creators want to ask for the same data. You may also wish to use the same fields later on another form.
1. First make sure has someone else already created the fields you need by selecting Ready-to-use-fields under the Fields tab. You can see all stored fields by leaving the search box blank.
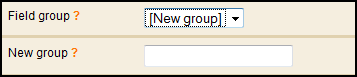
2. If no-one has yet saved fields, you can do it. In the editing status of the field group, select Group reuse. Save the fields either for your own use or for everybody in your organization.
When adding a new field group, either select an existing field group from the drop down menu or create a new field group by selecting New group.
4. Field types
Several field types allow you to select both the visible value and selection value. For example, the values in a drop-down menu might be displayed in text format, but for the report you may wish to have numerical values, which are easier to handle in e.g. Excel. For example:
Visible value, shown to the respondent
Fair
Average
Good
Selection value, saved in the report
1
2
3
-> you can easily use the report or Excel to calculate the average, e.g. 2,3.
You can add new field by clicking on the desired field type on the right side of the Fields tab.
Text field
A simple basic field, suitable for example for contact information.
Use the text field only if you cannot know the respondents’ choices beforehand. Handling the report will be easier if you can offer the respondents reply options by, e.g. a drop down menu.
Drop down menu
Drop down menu contains already defined options.
A drop down menu can be obligatory. In that case, the first option for the user is Select.
Check box group
A number of boxes, out of which the respondent chooses several or none.
You can define the minimum and maximum number of boxes the respondent can check. The boxes may be divided into columns.
Text field table
By using text field tables, you can create an Excel-type of view, in which rows and columns have titles. For example: the rows Event 1, Event 2 etc. have each beginning date, ending date, description.
Text area
For texts longer than a few words, text area is the best option. If you want to, you can offer the respondent the possibility to format the text by selecting WYSIWYG.
- Make sure the area is large enough for its purpose.
- Don’t use the WYSIWYG editor unless you have to: it makes the report more difficult to read.
Check box
A single, checkable field. Example: choice I want more information.
Radio buttons
With radio buttons, the respondent can select only one of the given options. You can create several rows with the same options, e.g.
- row headers
- column headers
- clarification column
Description
Texts you can use to give more information and instructions to the respondents.
The respondent cannot edit the field and it is not saved in the report.
Ready-to-use fields show the field groups you have saved and the field groups other users have shared.

